In today’s fast-moving tech world, organizations need tools that make IT resource provisioning faster and smarter. vRealize Automation—now called VMware Aria Automation—is built exactly for this purpose. It helps teams manage hybrid cloud environments while keeping security compliance at the center. Companies in the United States, especially large enterprises and startups scaling fast, use this platform to deliver applications and services with speed and control.
Unlike traditional systems, vRealize Automation is more than just self-service provisioning. It combines DevOps infrastructure management with multi-cloud automation to handle both public and private clouds. This allows IT departments, developers, and business units to work together smoothly without waiting days or weeks for infrastructure setup.
Evolution and History of vRealize Automation
The journey of vRealize Automation began with VMware’s acquisition of DynamicOps. Over time, VMware shaped the product to suit the growing demand for automation workflows and cloud-native applications. Earlier versions, especially vRA 7.x, provided basic VM provisioning and configuration management. However, businesses wanted more scalability and tighter cloud orchestration.
VMware responded with vRA 8, a modern, microservices-based platform. It integrated Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and infrastructure pipelining features, transforming it into a full DevOps lifecycle automation solution. Later, VMware rebranded the platform under the VMware Aria Automation umbrella, aligning it with a broader ecosystem of cloud tools.
Core Features of vRealize Automation
What makes vRealize Automation unique is its blend of cloud templates, automation pipelines, and policy-based access control. These features allow IT teams to quickly deploy apps across multiple clouds. With catalog management, users can request resources, and policies ensure every deployment aligns with business standards.
The platform also excels at Kubernetes automation, giving developers full support for modern container-based applications. In addition, centralized governance ensures that every project follows proper rules while enabling flexibility. This balance makes it easier for US-based enterprises to achieve both speed and compliance enforcement.
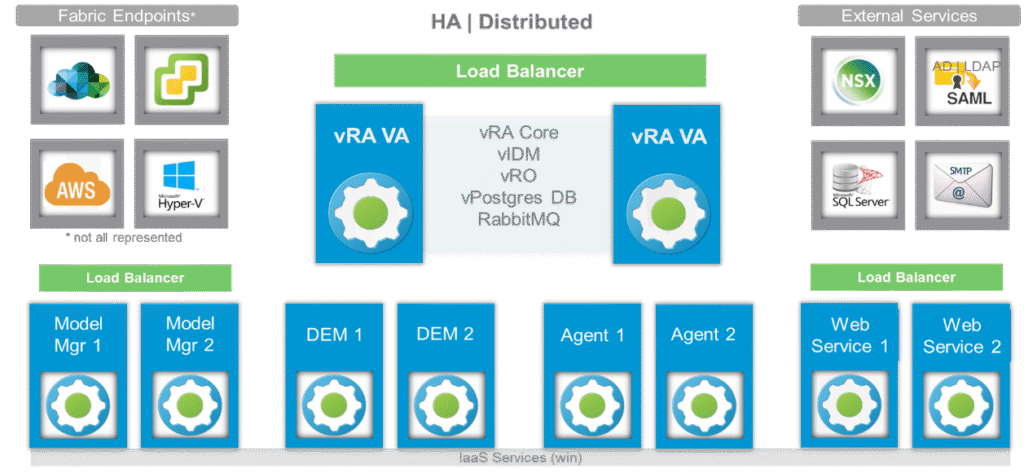
Understanding vRA 8 Architecture

The vRA 8 architecture is built on microservices. It includes key elements such as Cloud Assembly, Service Broker, and Code Stream. These work together to handle automated provisioning, workload deployment, and cloud orchestration.
Compared to earlier designs, vRA 8 supports infrastructure lifecycle management with stronger multi-cloud governance. Its scalable design allows seamless integration with platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, alongside vSphere compute virtualization.
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Assembly | Builds cloud templates | Create VM blueprints |
| Service Broker | Provides a single catalog for requests | Self-service IT |
| Code Stream | Automates software release process | Manage CI/CD pipelines |
How vRealize Automation Works
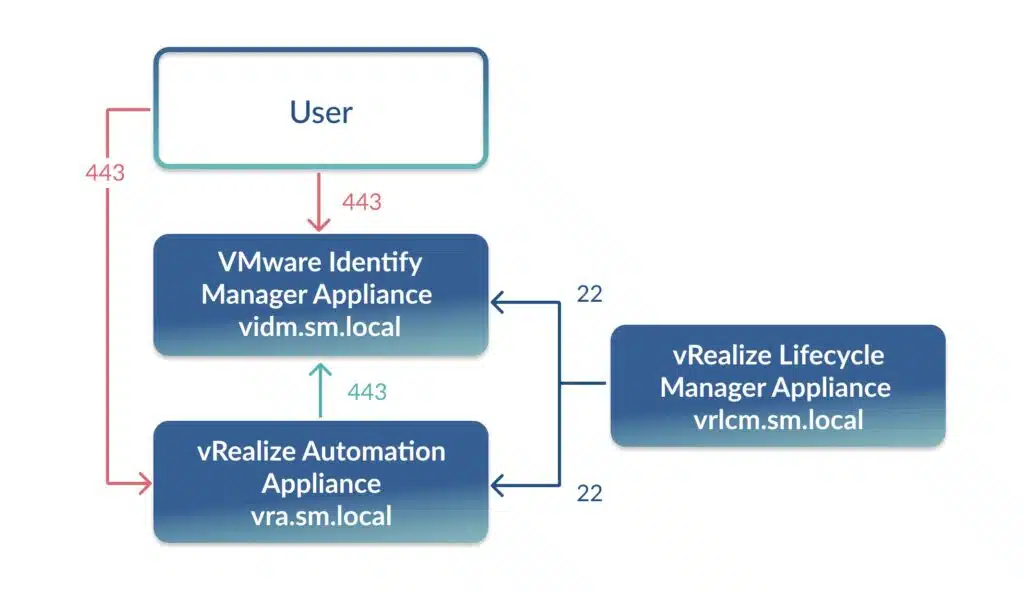
At its core, vRealize Automation follows a simple flow. A user requests resources through the Service Broker catalog. Then Cloud Assembly provisions the required infrastructure across chosen cloud vendor integration platforms. Finally, developers use automation pipelines to roll out applications quickly.
For example, a team in a US healthcare company can use cloud templates to deploy patient record apps across AWS and VMware Cloud. This cuts delivery time from weeks to hours, while keeping costs under control through cloud cost optimization.
Benefits of Using vRealize Automation for IT and Businesses
The first clear benefit is speed. With continuous integration and delivery, applications move from concept to production much faster. This reduces downtime and improves customer satisfaction. Automation workflows also free IT teams from repetitive tasks so they can focus on strategic projects.
The second benefit is control. Multi-cloud governance makes sure businesses avoid shadow IT while achieving visibility over usage. For US companies handling sensitive data, compliance enforcement and vulnerability remediation are crucial. Policy-based access control ensures that resources are only used by the right teams.
Key Use Cases of VMware vRealize Automation
Many US organizations adopt vRealize Automation for DevOps lifecycle automation. Developers can run CI/CD pipelines without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This results in more frequent updates and fewer production errors.
Another popular use case is Kubernetes automation with Tanzu Kubernetes. Businesses can manage cloud-native applications at scale, while ensuring cloud governance. In addition, finance companies often use it for cloud cost optimization, reducing waste across public and private clouds.
Automating DevOps and Multi-Cloud Environments with vRA
In a DevOps setting, vRealize Automation connects with third-party tool integration (Ansible, Puppet), Git, and Jenkins. This makes it easy to create automation pipelines that handle testing, deployment, and rollback. Developers save time, while operations keep systems secure.
In multi-cloud automation, companies can roll out workloads to Azure, AWS, or on-premises VMware data centers. For example, a retailer in the USA can deploy e-commerce workloads across regions, ensuring consistent performance through cloud orchestration.
vRealize Automation Service Broker and SaltStack Config
The Service Broker acts as a one-stop shop for all resources. Teams request infrastructure, apps, or services in a simple way, while admins apply rules for compliance enforcement. It ensures smooth catalog management and effective self-service provisioning.
For organizations looking to maximize the impact of vRealize Automation, leveraging tools that enhance content strategy can make a big difference. By using the Ben Stace Semantic SEO tool, teams can better understand the context and relevance of their keywords, identify related terms, and optimize documentation or internal knowledge bases. Integrating insights from this tool ensures that your content not only aligns with best SEO practices but also supports effective multi-cloud governance and DevOps lifecycle automation, making technical guides and IT documentation far more discoverable and valuable to users.
Integrating vRealize Automation with VMware vSphere, vCloud Suite, and Third-Party Tools
Integration with vSphere Compute Virtualization
vRA directly works with vSphere compute virtualization to deploy and manage workloads. This link makes VM creation, scaling, and infrastructure lifecycle management smoother.
vCloud Suite for Deeper Visibility
By pairing vRA with the vCloud Suite, businesses get insights into resource use, costs, and performance. This ensures cloud cost optimization and better cloud governance.
Third-Party Tool Integration
Through third-party tool integration (Ansible, Puppet) and SaltStack Config, organizations extend automation to configuration management, security compliance, and container-based applications like Tanzu Kubernetes.
Limitations and Challenges of vRealize Automation
While powerful, vRealize Automation isn’t without challenges. Some US companies find the initial setup complex, particularly those new to cloud orchestration. Training is often needed for staff to fully use features like automation workflows and CI/CD pipelines.
Another limitation is cost. Licensing and support for large-scale multi-cloud automation can be high. Smaller businesses may prefer alternatives, although they miss out on the advanced compliance enforcement and policy-based access control that vRA offers.
Future Trends and Roadmap of VMware Aria Automation
The future of VMware Aria Automation lies in smarter cloud orchestration. Analysts predict AI-driven tools will help optimize workload deployment and cloud cost optimization automatically. This trend will make infrastructure pipelining even faster.
In the US market, demand for secure self-service IT and reliable software release processes continues to rise. With new innovations in event-driven automation and deeper third-party tool integration (Ansible, Puppet), VMware is positioning vRA as the backbone of modern enterprise IT.

